Remote work offers businesses flexibility and access to global talent pools. However, it also expands the potential attack surface for cybercriminals.
With remote teams accessing sensitive company data from various locations and devices, comprehensive cybersecurity measures are essential.
Cyber threats targeting remote work setups are becoming more sophisticated. From advanced phishing schemes to AI-powered attacks, the challenges facing remote teams are diverse and constantly changing.
In this blog, we will dive into the most effective cybersecurity strategies to protect your remote team and keep your business secure.
Remote Work Cybersecurity Risks and Challenges
According to a recent study, 67% of organizations reported an increase in the frequency, severity, and scope of cyberattacks since shifting to remote work. This surge in cyber threats has exposed vulnerabilities that many companies were unprepared to address.
The distributed nature of remote teams, combined with the use of personal devices and home networks, has created a complex web of potential entry points for cybercriminals.
Common cybersecurity risks in remote work settings include:
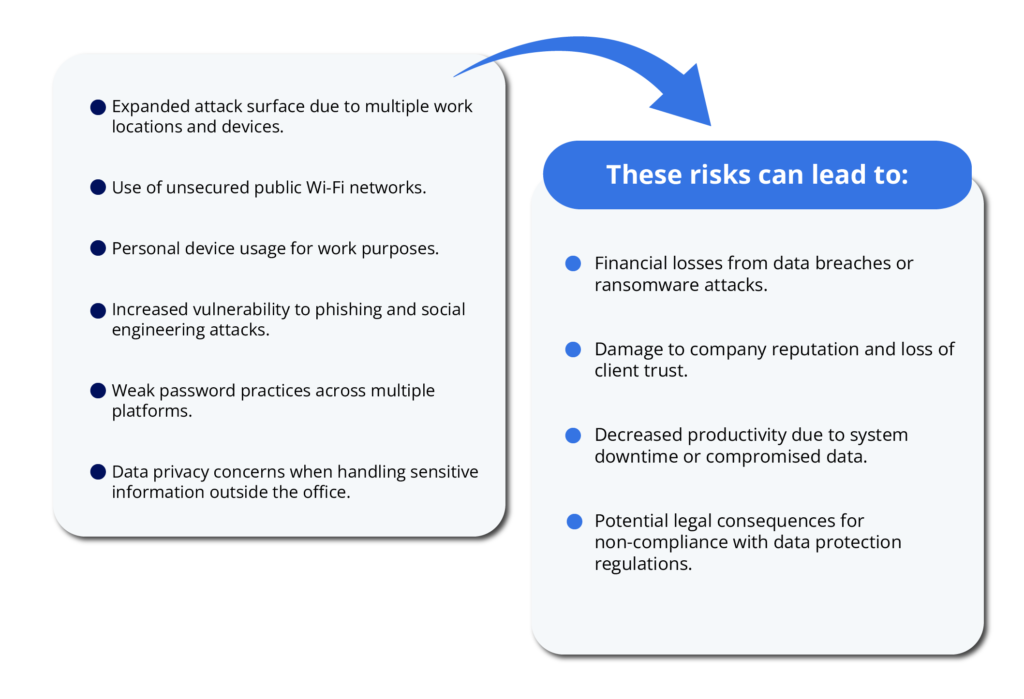
The impact of these risks is substantial. IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 found that the average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million, a 15% increase over 3 years.
For companies with remote work models, this figure was even higher, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity measures tailored to remote work environments.
Top 4 Cybersecurity Strategies for Remote Teams for 2024
Protecting remote teams from cyber threats requires a comprehensive approach that combines advanced technologies with robust policies and employee education.
The following strategies represent the most effective methods for safeguarding your remote workforce in 2024 based on current trends and emerging threats.
1. Implement Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture is a security model that assumes no user, device, or network is trustworthy by default. This approach has gained significant traction, with Gartner predicting that 60% of organizations will embrace Zero Trust as a starting point for security by 2025.
Implementing Zero Trust can dramatically reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access in remote work environments.
Key components of a Zero Trust strategy include:
- Continuous authentication and authorization for all users and devices.
- Micro-segmentation of networks to limit lateral movement.
- Least privilege access principles to minimize potential damage from compromised accounts.
- Real-time monitoring and analytics to detect and respond to anomalies quickly.
- Encryption of data both in transit and at rest.
2. Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an essential layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to resources.
According to Microsoft, MFA can block over 99.9% of account compromise attacks.
For remote teams, MFA is a crucial defense against unauthorized access, especially when employees are using personal devices or connecting from various locations.
Best practices for implementing MFA include:
- Requiring MFA for all remote access to company resources.
- Using a combination of factors (e.g., something you know, something you have, something you are).
- Implementing adaptive MFA that considers context such as location, device, and behavior.
- Educating employees on the importance of MFA and how to use it effectively.
- Regularly reviewing and updating MFA policies to address new threats.
3. Deploy Comprehensive Endpoint Security Solutions
With remote work, every device becomes a potential entry point for cyber attacks.
Comprehensive endpoint security solutions protect individual devices that connect to your network, including laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
These solutions have evolved beyond traditional antivirus software to include advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
Key features to look for in endpoint security solutions:
- Next-generation antivirus protection.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR) capabilities.
- Application control and whitelisting.
- Data loss prevention (DLP) tools.
- Mobile device management (MDM) for BYOD scenarios.
- Automated patch management and software updates.
4. Conduct Regular Security Awareness Training
Human error remains one of the biggest cybersecurity risks, making ongoing security awareness training crucial for remote teams.
A well-informed workforce can serve as a strong first line of defense against cyber threats.
According to the 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, 74% of breaches involved the human element, highlighting the importance of employee education.
Effective security awareness training should cover:
- Recognizing and reporting phishing attempts and social engineering tactics.
- Best practices for creating and managing strong passwords.
- Safe browsing habits and the risks of public Wi-Fi networks.
- Proper handling of sensitive data and compliance with data protection regulations.
- The importance of keeping software and systems up to date.
- Incident reporting procedures and the role of employees in the company’s cybersecurity strategy.
Emerging Technologies in Cybersecurity for Remote Work
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Threat Detection
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing cybersecurity by enabling more rapid and accurate threat detection and response.
These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate a security breach.
Key applications of AI and ML in cybersecurity include:
- Real-time threat detection and prevention.
- Automated incident response and remediation.
- Predictive analytics to anticipate potential vulnerabilities.
- User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to detect insider threats.
- Intelligent automation of routine security tasks.
- Continuous learning and adaptation to new threat patterns.
Biometric Security for Enhanced Authentication
Biometric security technologies offer a more secure and user-friendly alternative to traditional password-based authentication methods.
For remote teams, biometrics can provide an additional layer of security, especially when accessing sensitive data or systems from various locations.
Advantages and applications of biometric security include:
- Increased accuracy in user identification and authentication.
- Reduced risk of credential theft or sharing.
- Seamless integration with existing security systems.
- Support for multi-factor authentication strategies.
- Enhanced user experience with faster, password-free logins.
- Compliance with stringent data protection regulations.
Blockchain Technology for Secure Communication and Transactions
While primarily known for its role in cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology offers promising applications in cybersecurity, particularly for ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of communications and transactions in remote work settings.
Potential applications of blockchain in cybersecurity include:
- Decentralized identity management and authentication.
- Secure, tamper-proof logging of system activities and changes.
- Protection against data manipulation and unauthorized access.
- Enhanced supply chain security for software and hardware.
- Secure sharing of sensitive information across distributed teams.
- Immutable audit trails for compliance and forensic purposes.
How to Choose a Cybersecurity Agency for Remote Team Protection
Selecting the right cybersecurity agency is crucial for organizations with remote teams.
A specialized agency can provide tailored solutions to address the unique challenges of distributed workforces, ensuring robust protection against evolving cyber threats.
The right partner will not only implement effective security measures but also align their approach with your business objectives and remote work culture.
When evaluating cybersecurity agencies for your remote team protection, consider the following factors:

Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity for remote teams can’t just be another item on your to-do list.
The threats are real, and they’re evolving fast. But here’s the thing: with the right strategies and partners, you can turn this challenge into a competitive advantage.
Remember, you don’t have to figure this out alone.
If you’re looking for top-notch cybersecurity agencies or other RevOps experts, check out the CloudTask Marketplace.
We’ve got a goldmine of talent ready to help you secure your remote teams and take your business to the next level.
Start exploring our Marketplace today and find the perfect match for your needs.